AMD's 890FX Chipset Makes Its Debut
The key feature setting apart the AMD 890FX from previous generation chipsets such as the 790FX is 6GB/s SATA support, which is provided by the SB850 south bridge.
Both support a total of 38 PCIe 2.0 lanes, but while the 790FX featured four PCIe 1.1 lanes for the A-Link Express II feature in the north bridge, A-Link Express III on the 890FX chipset calls for four PCIe 2.0 lanes.

These are the fundamental elements of the 890FX, and it is worth nothing that the 790FX and 890FX are virtually identical in every other respect.
The 890FX still uses HyperTransport 3.0 (5.2GT/s) to link the processor and north bridge together, while memory support is determined by the processor. Multi-GPU support is present but limited to Crossfire and Radeon graphics cards.
Whereas the 890GX chipset is limited to dual PCIe 2.0 x8 bandwidth when using a pair of graphics cards in Crossfire, the 890FX provides both graphics cards with full PCIe 2.0 x16 bandwidth.
On motherboards that carry four PCIe x16 ports, it is possible to use four graphics cards providing PCIe x8 bandwidth to each port.
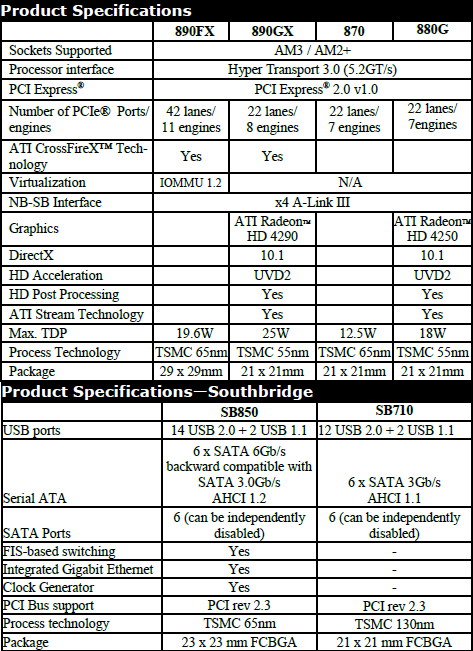
Also connected to the north bridge are two PCI Express 2.0 x1 slots and a single PCIe 2.0 x4 slot. Just like the 790FX, the 890FX features a total of 42 PCIe lanes, though only 38 of them are usable. As mentioned before, the other four lanes are used to connect the 890FX north bridge and SB850 south bridge together providing 2GB/s of bandwidth, something AMD calls A-link Express III.
In total the SB850 south bridge supports 14 USB 2.0 ports, two more than the SB750 used by the 790FX chipset. Therefore the key improvements on the SB850 is support for SATA 6.0Gb/s, extra USB 2.0 ports, and native Gigabit LAN support.
AMD I/O Virtualization Technology IOMMU (Input/Output Memory Management Unit) support is available in hardware with 890FX chipsets for those operating systems that can take advantage of it. IOMMU allows for virtual addressing of memory by system devices. This enables devices to use their native drivers in a virtualized environment for enhanced performance.
In a non-virtualized environment, IOMMU provides memory isolation and protection capabilities - device access to system memory is vetted by the IOMMU such that critical/unrelated memory information (e.g. kernel pages, protected content ...) can be protected, leading to an overall more robust system.