Forward-looking: Google has announced that it will lay a new cable on the Pacific Ocean seabed to provide more reliability and resiliency to internet connections across the Pacific region. The $400 million project is the result of a partnership between the tech giant, government organizations, and investment funds.

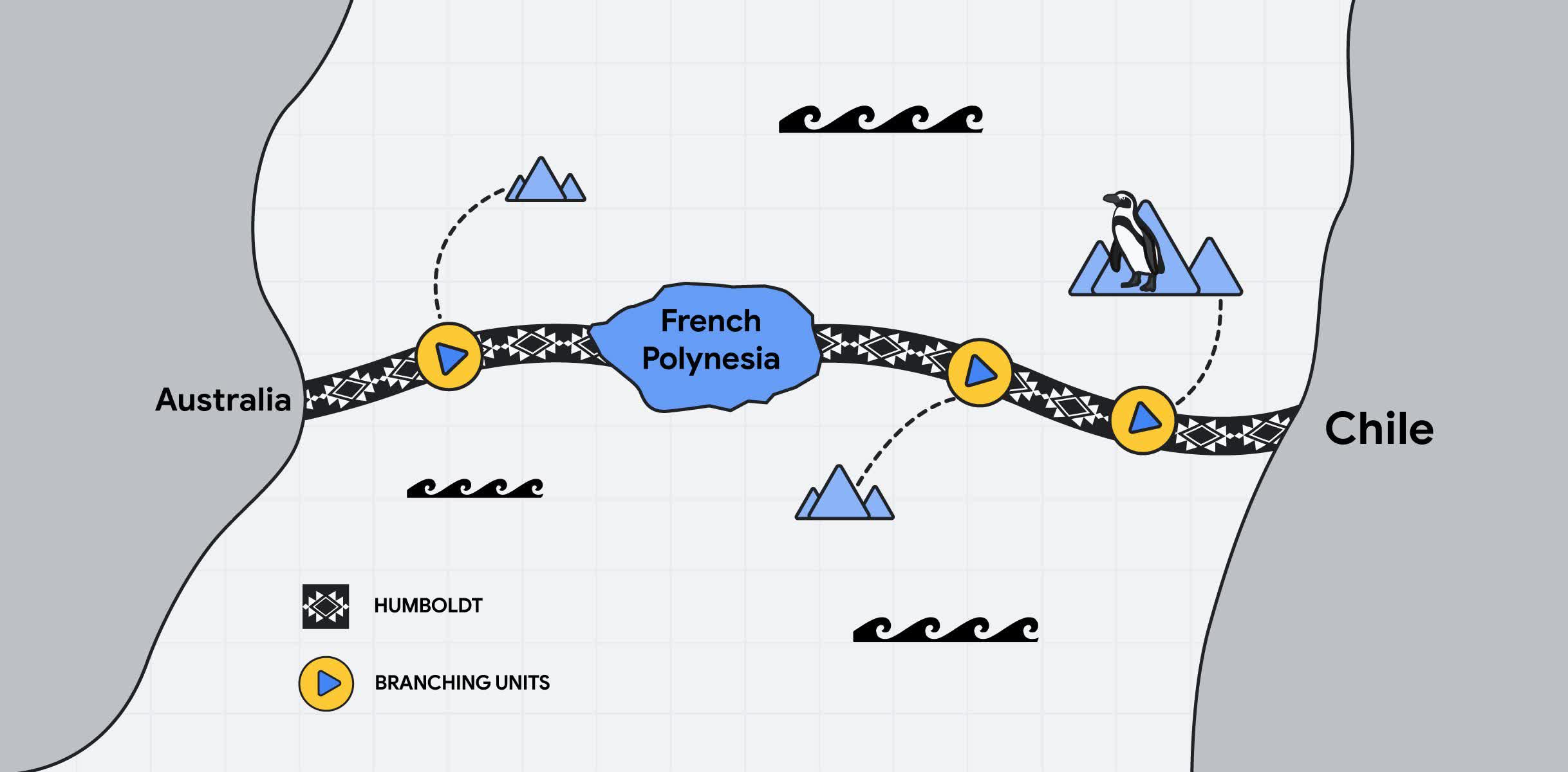
Google officially announced the "Humboldt" project, a joint initiative to build a new undersea internet infrastructure. The Mountain View corporation will work together with the Chilean infrastructure fund Desarrollo País of Chile, the Office of Posts and Telecommunications of French Polynesia (OPT) and other partners to link Australia and Chile with a new undersea cable spanning across 14,800 km of Pacific Ocean seabed.
Humboldt is the first direct cable route between South America and Asia-Pacific, Google said. The new cable confirms the company's commitment to Chile, as it will join existing digital infrastructure investments in the country and across Latin America. The Chilean government has been working on a direct fiber optic connection between South America and the Asia-Pacific region since 2016, and Humboldt will position the country as the gateway to Latin America for data coming from Asia Pacific.
According to the project's official page, Humboldt will provide "greater geographical diversity," a new resilience level, and redundancy to existing telecommunications networks through a new route. The increased internet capacity and improved latency will play a key role in managing the "explosive" increase in traffic coming from new communication technologies such as 5G and Internet of Things (IoT).
Google highlighted how subsea cables can help drive substantial economic growth, both in terms of gross domestic product (GDP) and job creation, adding that businesses and public organizations can enjoy and deliver better digital experiences while people can gain skills and knowledge for new career paths.
According to an estimation by Analysys Mason, previous undersea cables deployed by Google in Latin America and the Caribbean region (LAC) will lead to a cumulative increase in GDP of $178 billion between 2017 and 2027, with around 740,000 new jobs created by 2027.
Patricio Rey Sommer, General Manager of Desarrollo País, said that Google's public announcement about Humboldt marks a significant milestone for the project's history. After years of behind-the-scene work, Humboldt is now finally entering its "materialization phase." The cable should be completed by 2026.
The US State Department, which will join the project with a $15 million investment, said that the Humboldt cable represents a concrete example for "greater economic cooperation" in the Americas. The Humboldt name was chosen in a naming contest on Chilean social media, as a tribute to German explorer Alexander von Humboldt who traveled extensively to the Americas at the turn of the 19th century.