Forward-looking: Computers excel at taking a 3D model and rendering it on a 2D screen. What they are not so capable of is taking a 2D image and creating a 3D model. However, thanks to machine learning, this is now becoming possible.

Nvidia researchers have created a rendering framework that uses AI to take 2D information and transform it into a 3D object accurately. The system is called DIB-R, short for differentiable interpolation-based renderer and is built on PyTorch, a machine learning framework. The team will be presenting its findings at the annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems in Vancouver, Washington, this week.
Essentially the framework does the opposite of what GPUs usually do. It analyzes an image and then forms a high-fidelity 3D object, including shape, texture, color, and lighting. The encoder-decoder architecture starts with a polygonal sphere and morphs it using the given information in the 2D image.
The process only takes one-tenth of a second, but the neural network takes two days to train using a single Nvidia V100 GPU. Nvidia claims that training using other GPUs would take several weeks. After feeding it several datasets containing pictures of birds, DIB-R was able to accurately create 3D models when given a single image.
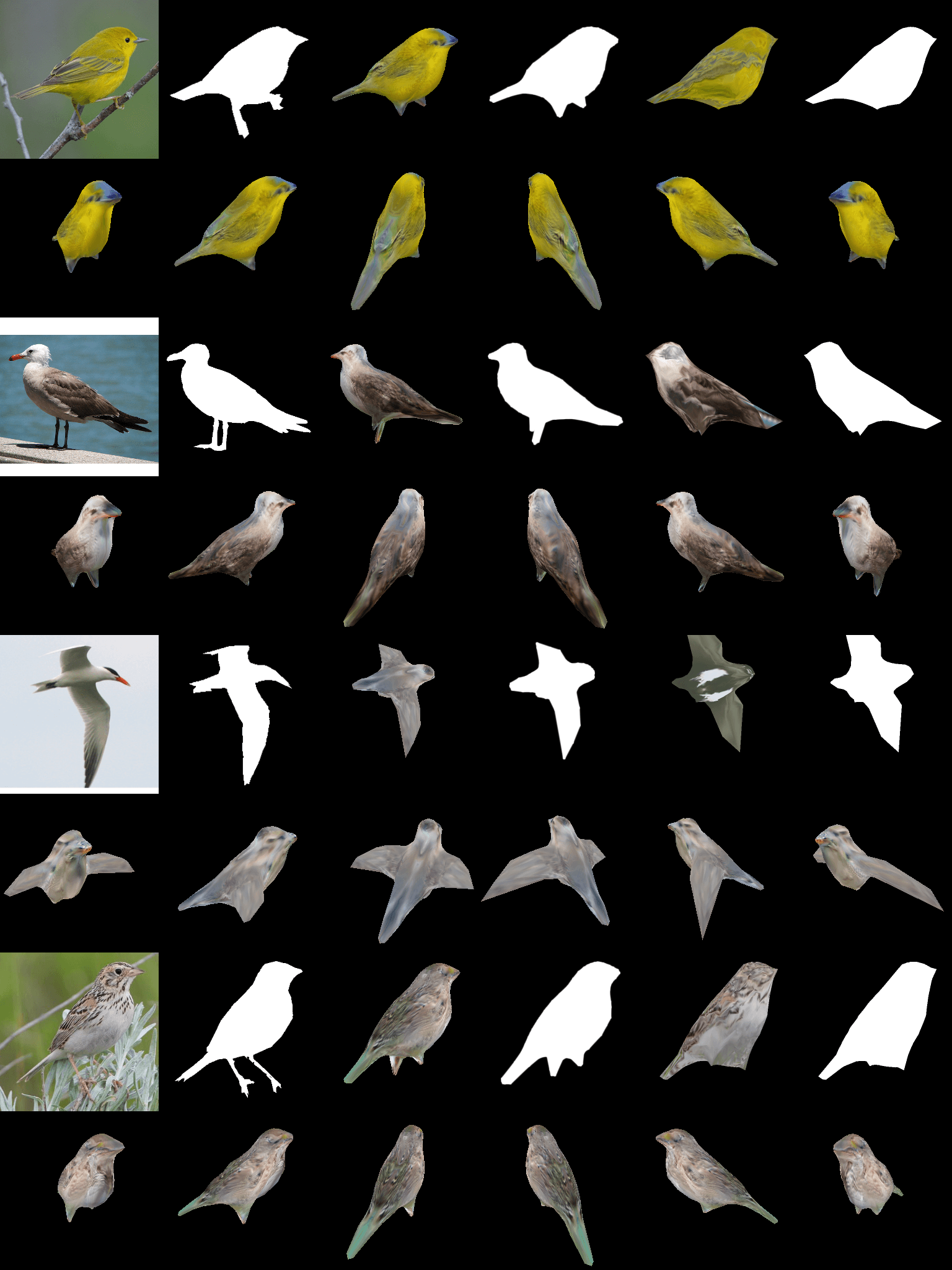
While birds were the focus of the experiment, co-author of the research paper on the subject, Jun Gao said that the system can render any 2D image into a 3D model.
“This is essentially the first time ever that you can take just about any 2D image and predict relevant 3D properties,” said Gao.
The researchers believe that the system can be used to give depth perception to autonomous robots improving safety and accuracy when working in an environment. Being able to understand the three-dimensionality of things around it will allow robots to better navigate as well as manipulate the objects they are tasked with handling.
Nvidia has added DIB-R to Kaolin, its 3D deep learning PyTorch GitHub library. Kaolin helps researchers accelerate 3D deep learning experiments.