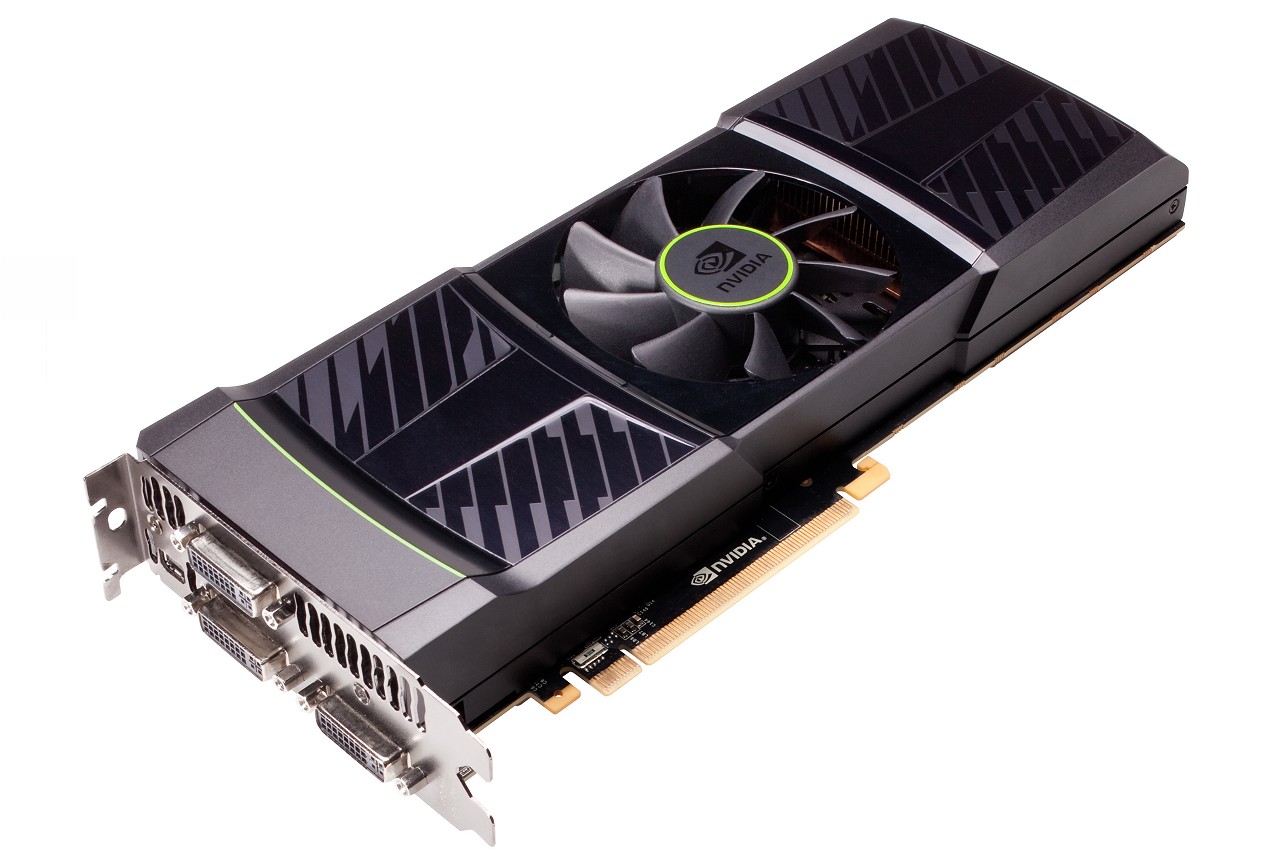
GeForce GTX 590 In Detail
With a suggested retail price of $699, the GeForce GTX 590 is obviously aimed at the Radeon HD 6990. Nvidia says its dual-GPU package was created for elite enthusiast gamers looking to run titles at their maximum graphics settings and screen resolutions with high levels of anti-aliasing.
The company goes on to say "this is a very high-end product that's catered towards the most discriminating gamer. Think of it as the Bugatti Veyron of the graphics world." In six years, only 291 Veyrons have been delivered, so let's hope the GTX 590 doesn't share that particular feat.

The reference design measures just 11" long making it much shorter than the 12.2" Radeon HD 6990, so Nvidia's card should fit inside a broader range of computer cases. In fact, it's only a half an inch longer than Nvidia's official specifications for the single-GF110 GeForce GTX 580.
Based on Fermi's third-generation Streaming Multiprocessor (SM) architecture, the GeForce GTX 590 boasts 8 Graphic Processing Clusters, 32 Streaming Multiprocessors, and 1024 CUDA cores. There are also 96 ROP (Raster Operations) units and 128 TAU (Texture Addressing Units).
That's double the specifications seen on the GTX 580, but as we mentioned earlier, the GTX 590 has reduced clock frequencies. The graphics clock speed for fixed function units is set at just 607MHz which is 21% lower than the 772MHz that they operate at on the GeForce GTX 580.

The GeForce GTX 590 is paired with two banks of 1536MB of GDDR5 memory clocked at 1707MHz (3414MHz DDR) for a total memory capacity of 3072MB. Combine that with a 384-bit memory interface and you get a peak theoretical bandwidth of 327.7GB/s or163.9GB/s per GPU.
The GTX 590's GDDR5 memory is clocked 15% lower than the GTX 580's. Ultimately, this means that while the GTX 580's single GPU is fed a bandwidth of 192.4GB/s, each of the GTX 590's GPUs get 15% less bandwidth. When combined, they provide 70% more throughput.
Nvidia claims the GTX 590 has a Thermal Design Power (TDP) of 365 watts, which is 50% greater than the GTX 580. However, that's slightly lower than the 375-watt rating AMD slapped on its Radeon HD 6990.
Nvidia has employed the same cooling measures used by other high-end GTX 500 series graphics cards. The card has a number of power monitoring chips that oversee power draw from the PCIe slot and PCIe power connectors.

By monitoring power consumption, the card determines if it is drawing too much power and throttles down. We first saw a similar design on the Radeon HD 5970, which would regularly reduce its operating frequency when running load programs such as FurMark and OCCT. Using these programs to measure the load consumption of the GeForce GTX 590 can't really be done accurately.
Other than the PCIe slot, the GeForce GTX 590 pulls power though a pair of external PCIe power connectors. The GTX 590 requires a pair of 8-pin connectors, just like the new Radeon HD 6990. Nvidia recommends using at least a 700-watt power supply with the GTX 590.
Nvidia has employed a 12-layer PCB for best signal integrity. Powering the twin GPUs is a 10-phase advanced digital power controller with overvolting capability, while two dual-phase controllers provide power for the board's GDDR5 memory.
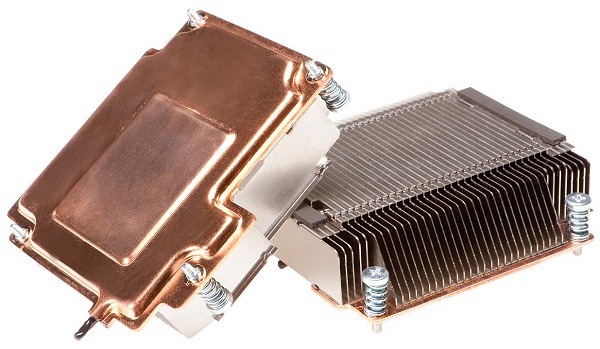
The GTX 590 has also received a substantially overhauled cooling design. Notice there are no heatpipes sticking out the top and the PCB ventilation has been removed. Instead of using a traditional heatpipe heatsink, the GTX 590 utilizes two vapor chamber heatsinks.
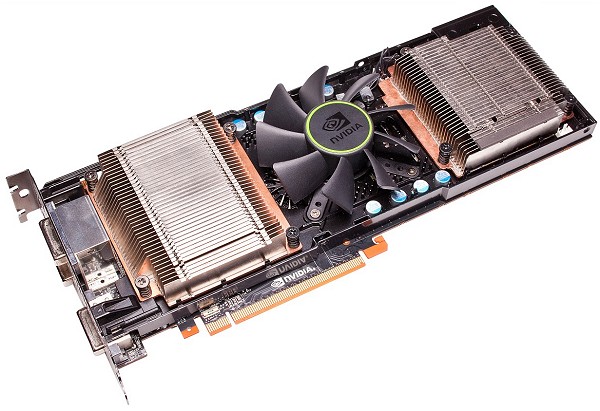
With the heatsinks off, the GeForce GTX 590 looks considerably different than the previous dual-GPU solutions. In fact, the design is remarkably similar to the Radeon HD 6990's as each GPU is now located at opposite ends of the 11" PCB.

The heatsinks are separated by a large 85mm fan which is positioned in-between them rather than at the end of the card. This design is said to be more efficient as it allows the fan to spin at a lower RPM while providing the same amount of air across both heatsinks.
The GTX 590 has three dual-link DVI-I outputs along with one Mini DisplayPort connection and there's also a small amount of ventilation across the top of the I/O panel. The card can handle three displays for a maximum resolution of 7680x1600 (three 2560x1600 LCDs) – something we plan to test.
