During last year's Hot Chips conference, Samsung executive Jin Kim said GDDR6, a successor to the commonly used GDDR5 memory found in many GPUs, would arrive next year with a throughput of around 14Gbps. But it turns out that Samsung has spent the last 15 months speeding up the next generation of DRAM, which can now reach 16Gbps.
The new detail was part of a Samsung announcement revealing that 36 of its products had already been recognized as Innovation Award winners ahead of January's CES trade show. In among this year's Galaxy phones and its 8TB NGSFF NVMe SSD is the 16Gb GDDR6, which is described as the fastest and lowest-power DRAM for graphics-intensive applications.
"It processes images and video at 16Gbps with 64GB/s data I/O bandwidth, which is equivalent to transferring approximately 12 full-HD DVDs (5GB equivalent) per second," writes Samsung.
For comparison, GDDR5 can reach up to 9Gbps in the newer version of the GTX 1060. And with 8GB of the refined GDDR5X, the GTX 1080 has a throughput of 10Gbps, whereas the 1080Ti flagship boasts 11GB of GDDR5X and 11Gbps.
Not only is GDDR6 faster than today's graphics memory, but it also consumes less power. While the current version uses 1.5V for 8Gbps GDDR5, its successor operates at just 1.35V.
We should start seeing GDDR6 appearing in GPUs launching next year, including Nvidia's highly anticipated Volta-based consumer cards. As noted by Wccftech, GDDR6 will come in 8Gb and 16Gb densities while the standard followed by JEDEC allows for up to 32Gb dies.
Samsung also used the 2016 Hot Chips conference to tease the third generation of High Bandwidth Memory: HBM3. It improves the density, bandwidth, and power efficiency of HBM1 and HBM2, while being cheaper to produce. It allows GPUs with up to 64GB of memory.
To give you an idea of how the current and upcoming memory technologies stack up against each other, check out the table below.
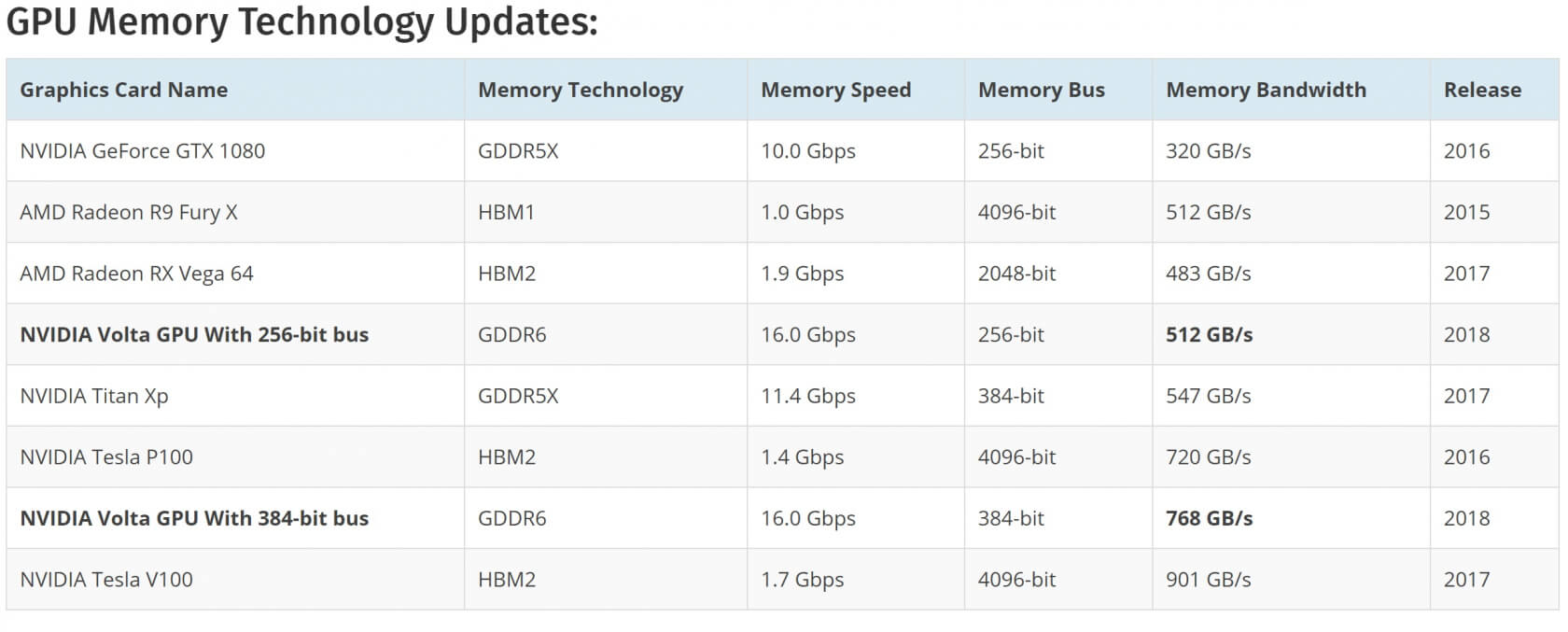
Table courtesy of wccftech