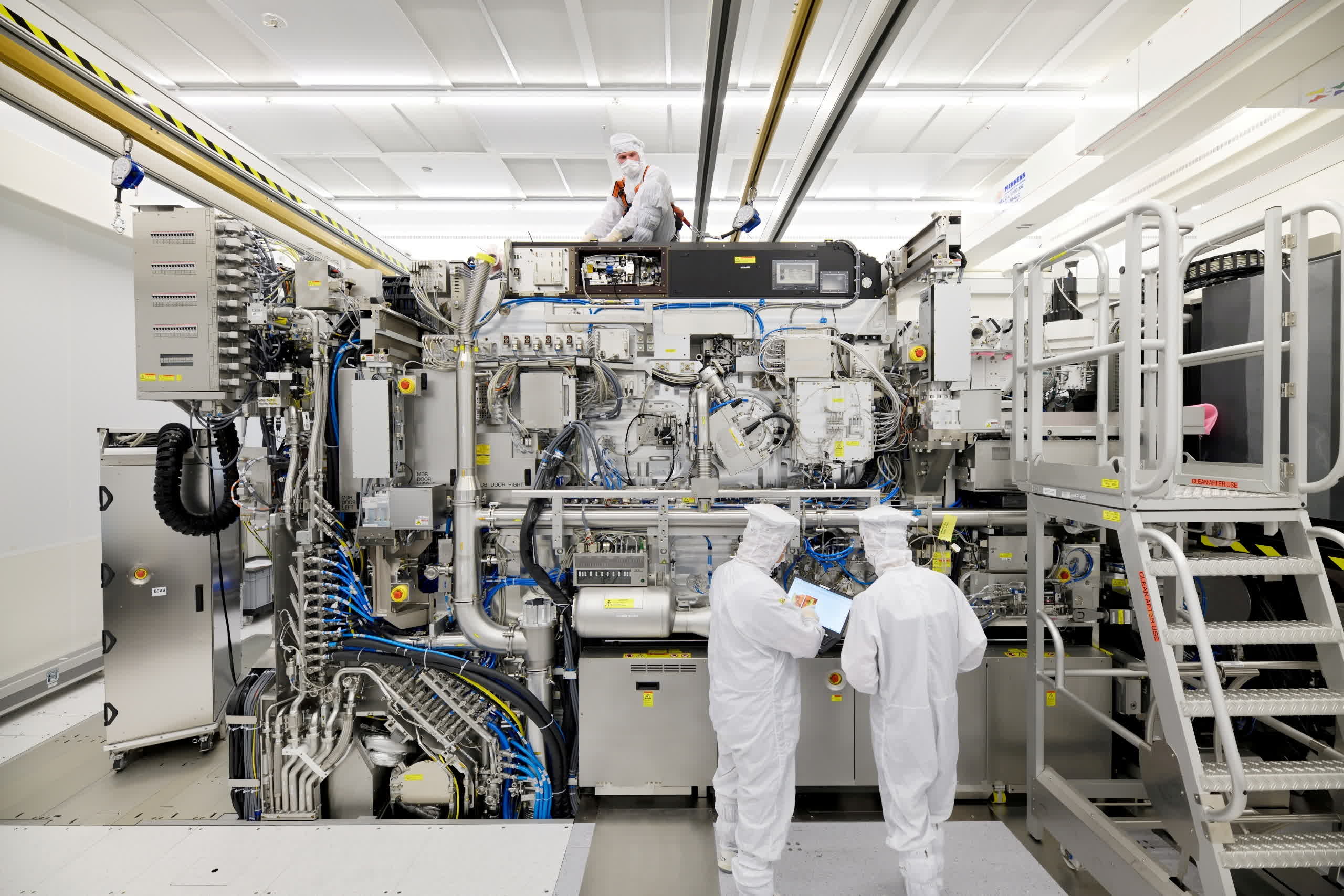
What just happened? The Netherlands' government has announced export controls on chipmaking machinery to China, weeks after reaching an agreement with the US to implement restrictions against the country. The new rules will build upon current restrictions that prevent the most cutting-edge products from being exported to the Asian nation.
At the end of January, it was reported that the US had completed two years of negotiations with the Netherlands and Japan to join the United States in imposing restrictions on the export of chip-manufacturing tools to China. The US says this will prevent its global rival from developing semiconductors for military applications, including supercomputers, nuclear weapons modeling, and hypersonic weapons.
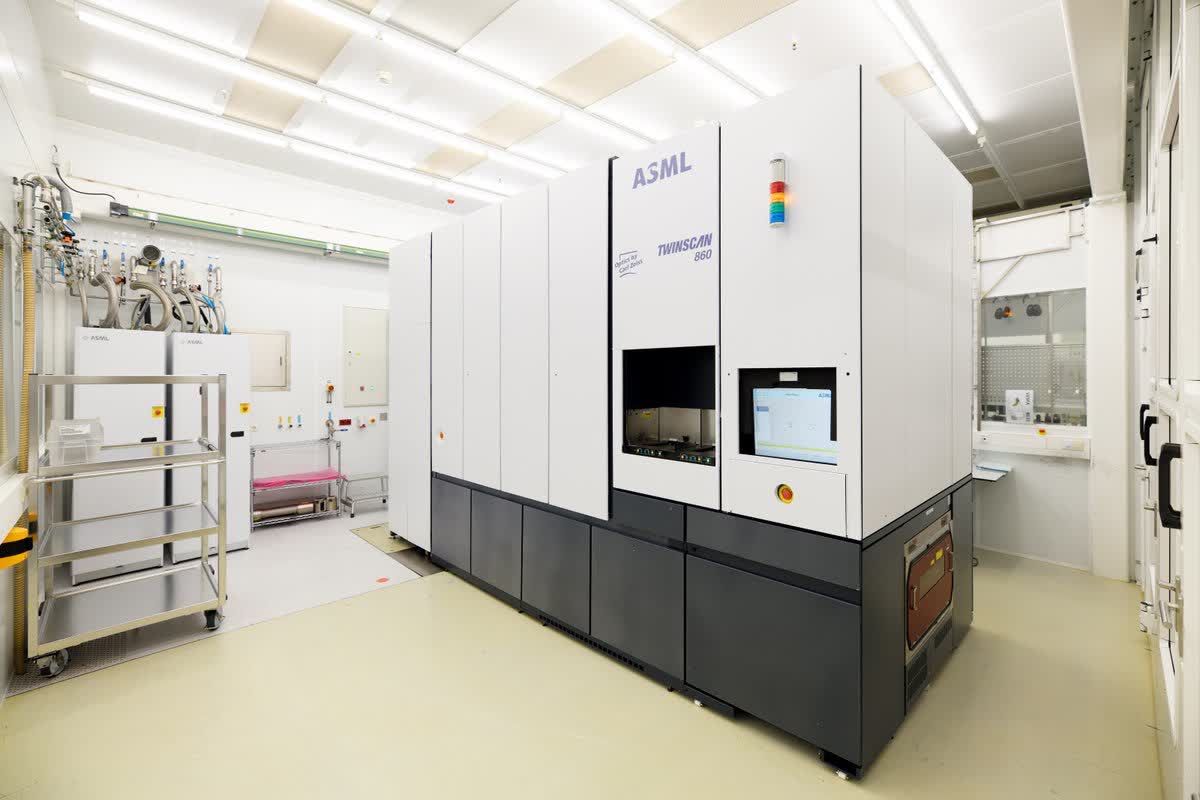
The Netherlands, home to chipmaking giant ASML, has become the first of the two countries to make an official announcement about its new export rules. Companies in the Netherlands are already prohibited from selling their most advanced extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography equipment, which costs about $164 million per unit, to Chinese customers as they cannot obtain an export license from the Dutch government due to pressure from the United States. The next step will be to restrict exports of older deep ultraviolet (DUV) lithography tools.

"Given the technological developments and geopolitical context, the government has concluded that it is necessary for the (inter)national security to expand the existing export controls on specific manufacturing equipment for semiconductors," Foreign Trade Minister Liesje Schreinemacher wrote in a letter to Dutch lawmakers. Neither China nor ASML were named in the letter.
ASML released a statement regarding the upcoming export restrictions, which will be introduced before the summer. It writes that the company will need to apply for export licenses for shipments of the most advanced immersion DUV systems. It does not expect the measures to have a material effect on its financial outlook for 2023 or longer-term scenarios.
ASML notes that the controls do not apply to all immersion lithography tools but only those classed as 'most advanced,' though it has not yet received additional information about this exact definition. This would mean the Netherlands' chip-related export restrictions aren't as strict as those imposed by the United States. It's unclear if ASML will still be able to service the $8.4 billion worth of DUV machines it has sold to Chinese customers since 2014.
The US will now be waiting for Japan to make a similar announcement. Some sources say it will come this week, but the country's trade minister says no decisions have been made yet.
Chinese chip firms have been preparing for the new restrictions from the Netherlands and Japan by stockpiling chip-making equipment, components, spare parts, and materials in warehouses. We recently heard that the export controls were having an effect: China's chip imports crashed by 27% in the first two months of 2023, a fall greater than the total decline for all of 2022.
