This is a good question! Most home computers only have two types of connectors for storage drives -- SATA and M.2 sockets. They have no limit to the capacity of the storage drive connected to them.
However, the operating system on the computer
does have a limit and it is determined by two things:
(1) If the motherboard supports UEFI or it only has BIOS;
(2) How the storage drive has been partitioned and formatted.
The way that data is arranged and stored on a drive is pretty complex, but let's just stick to the options you normally have in Windows when it comes to using a big storage drive. There are two main ways of partitioning a drive:
Master Boot Record (MBR) or
GUID Partition Table (GPT).
The drive limit for MBR depends on the
cluster size used (sometimes called the Allocation Unit Size) -- in recent versions of Windows, the default size is 4096 bytes, which sets a limit of 16 TB to the partition size.
Older versions using old hard drives might be using 512 byte clusters, which limits the drive partition to 2 TB.
You can use larger clusters to get bigger partitions, but it's better to be using GPT if you need anything bigger than a couple of TB. It doesn't matter what cluster size you use with GPT -- the maximum drive size is
billions of TB!
The quick way to check if your storage drives are set up as MBR or GPT is to press
Win key + R, type in
DISKPART, and then
list disk:
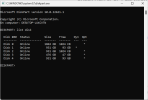
However, for your Windows computer to use GPT, then the motherboard needs to support
UEFI. You need to check with the manufacturer of the motherboard or read its manual to see if it supports UEFI and how to enable it. You can convert an MBR drive to a GPT one (
example guide).
